the 500Billion vs 5.6 Million AI Showdown: What China's Open-Source Surge Means For The Future
Explore the AI showdown between China's open-source surge and the massive investments shaping the global landscape. Discover how China's 5.6 million contributors are transforming AI innovation and challenging $500 billion investments worldwide.
By Dr Kreeno
The AI Arms Race: Money vs. Ingenuity
Imagine two chefs competing to make the world’s best meal. One spends 5.6 million budget, shares their recipes openly, and still wins over the crowd. This isn’t a culinary fantasy—it’s exactly what’s happening in the global AI race.
The U.S. is pouring [over 5.6 million. The twist? DeepSeek’s open-source strategy is proving that raw financial firepower might not be enough to win this war.
Let’s unpack what this David-and-Goliath dynamic means for AI’s future—and why it could reshape everything from your smartphone to global power structures.
David vs. Goliath: DeepSeek’s Open-Source Agility Takes on OpenAI’s Financial Firepower
In the timeless story of David and Goliath, a nimble underdog topples a towering giant using creativity and precision. Today, this dynamic plays out in the AI arena, where China’s DeepSeek R1—a $5.6 million open-source marvel—is challenging OpenAI’s 01, a product of America’s $500 billion AI spending spree. This clash isn’t just about budgets; it’s a battle of philosophies that could redefine how humanity builds and uses AI.
OpenAI, backed by Microsoft’s [Stargate Project](https://www.forbes.com/sites/craigsmith/2025/01/23/stargate-americas-500-billion-bid-to-corner-global-ai-capital/) , operates like a tech Goliath: centralized, proprietary, and fueled by unparalleled resources. Its models dominate benchmarks, but at eye-watering costs—training GPT-4 reportedly burned over $100 million. Meanwhile, DeepSeek’s R1, trained for less than the price of a suburban house, leverages open-source collaboration to achieve similar performance. By releasing core components publicly, DeepSeek taps into a global developer base that iterates on its framework for everything from [medical diagnostics to regional language support](https://time.com/7210296/chinese-ai-company-deepseek-stuns-american-ai-industry/) .
But how did David sharpen his slingshot? U.S. sanctions on advanced chips forced Chinese firms like DeepSeek to innovate with limited hardware. Instead of relying on brute-force computing, they refined algorithms to extract maximum efficiency from older chips—a skill that’s now their superpower. As [Yann LeCun, Meta’s chief AI scientist](https://www.businessinsider.com/meta-ai-yann-lecun-deepseek-open-source-openai-2025-1) , puts it: “Open-source communities move faster than any single lab. They’re the future.”
Yet Goliath isn’t defenseless. OpenAI’s closed models offer enterprise-grade reliability and safety controls, critical for industries like healthcare and finance. The question is whether giants can adapt before open-source Davids democratize AI’s future—or fracture it into incompatible ecosystems.
This showdown isn’t just about who wins. It’s about who gets to shape the rules of the game.
The $500 Billion Gamble: America’s Stargate Project
The U.S. approach to AI dominance is simple: throw money at the problem. Microsoft and OpenAI’s rumored Stargate Project aims to build a 500 billion push for AI supremacy. The goal? Train models with 100x the complexity of today’s systems.
But here’s the catch: bigger isn’t always better. As models grow more expensive, critics argue we’re hitting diminishing returns in AI performance. Training GPT-4 reportedly cost $100 million, and future models could require billions. For context, that’s like burning a Lamborghini’s worth of cash—every hour—for months.
China’s Open-Source Counterpunch: The DeepSeek R1 Phenomenon
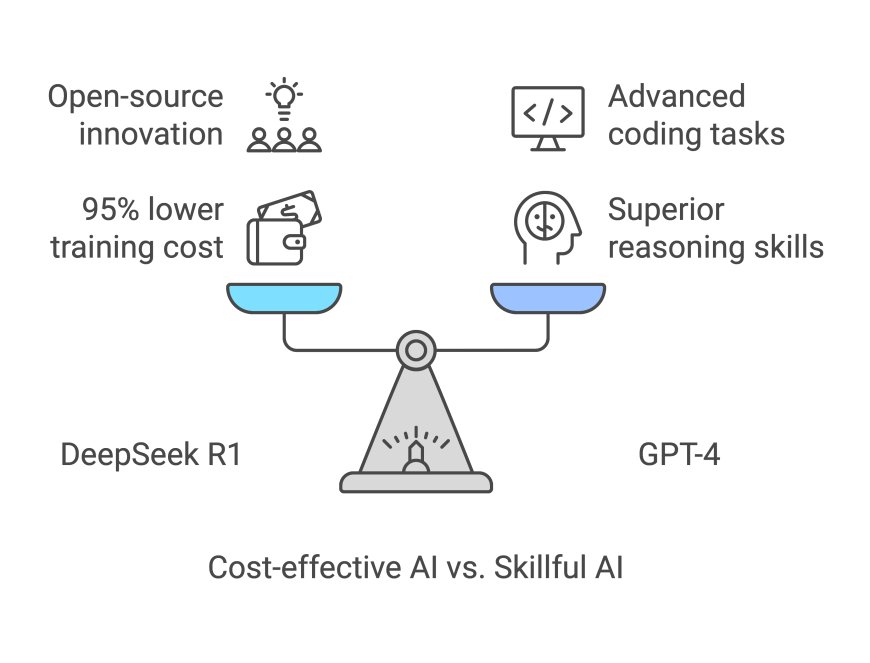
Enter DeepSeek, a Beijing-based AI lab that’s flipped the script. Their R1 model rivals GPT-4 in reasoning and coding tasks but costs 95% less to train. How? By embracing open-source innovation and ruthless efficiency.
What Is DeepSeek?
DeepSeek is a Chinese artificial intelligence lab. It was founded in 2023 and is based in Hangzhou, in China’s Zhejiang province. It has released an open-source AI model, also called DeepSeek. The latest version of DeepSeek, called DeepSeek-V3, appears to rival and, in many cases, outperform OpenAI’s ChatGPT—including its GPT-4o model and its latest o1 reasoning model.
However, the idea that the DeepSeek-V3 chatbot could outperform OpenAI’s ChatGPT, as well as Meta’s Llama 3.1, and Anthropic’s Claude Sonnet 3.5, isn’t the only thing that is unnerving America’s AI experts. It’s that fact that DeepSeek appears to have developed DeepSeek-V3 in just a few months, using AI hardware that is far from state-of-the-art, and at a minute fraction of what other companies have spent developing their LLM chatbots.
How Much Did DeepSeek Cost To Develop?
Perhaps the most astounding thing about DeepSeek is the cost it took the company to develop. According to the company’s technical report on DeepSeek-V3, the total cost of developing the model was just $5.576 million USD.
Yes, that’s million.
For less than $6 million dollars, DeepSeek has managed to create an LLM model while other companies have spent billions on developing their own. (In training just GPT-4, OpenAI reportedly spent $100 million alone, Wired noted in 2023.)
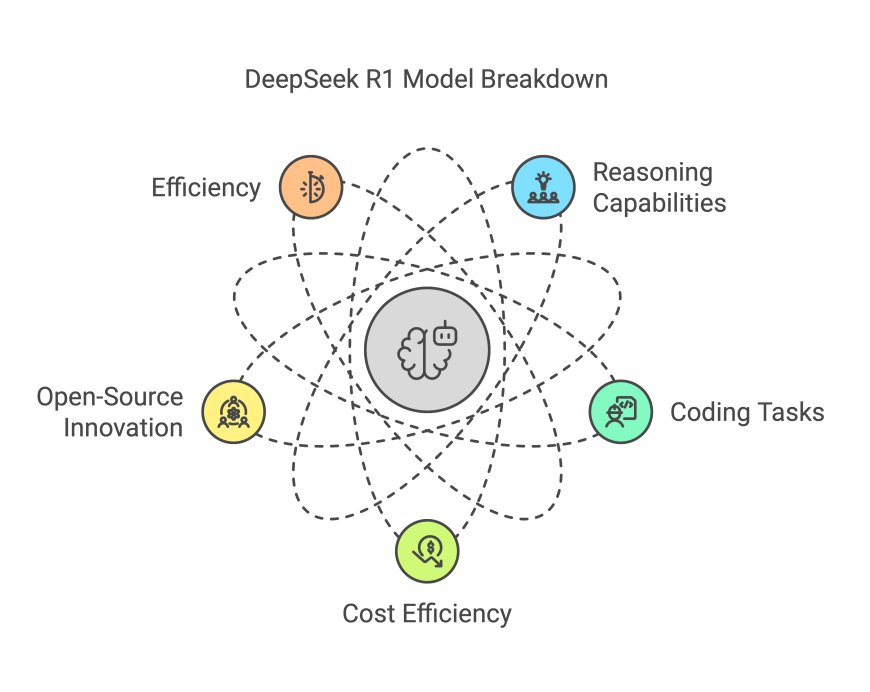
How Does DeepSeek R1 Work?
DeepSeek’s secret sauce is threefold:
-
Frugal Training: Instead of brute-forcing computations, they use smarter algorithms and data curation. Think of it as a chef who knows exactly which spices to use—no wasted ingredients.
-
Community Collaboration: By open-sourcing parts of their work, they tap into global brainpower. Developers worldwide fine-tune the model for niche tasks, from medical diagnostics to anime art.
-
Hardware Hacks: U.S. sanctions forced China to optimize for weaker chips. The result? Models that run efficiently on cheaper, sanction-proof hardware.
Is DeepSeek Open Source?
Partially. While not fully transparent, DeepSeek releases key components to the public—a stark contrast to OpenAI’s "walled garden." This hybrid approach balances innovation with commercial control.
Head-to-Head: DeepSeek R1 vs OpenAI O1
Let’s break down how these rivals stack up:
| Metric | DeepSeek R1 | OpenAI O1 |
|---|---|---|
| Training Cost | $5.6 million | $100 million+ |
| Accessibility | Open-source framework | Closed, proprietary system |
| Compute Efficiency | 8x faster per task | Requires high-end GPUs |
| Use Cases | Broad, community-driven | Enterprise-focused |
| Geopolitical Impact | Bypasses U.S. sanctions | Relies on Western infrastructure |
Sources: TIME, Stanford AI Index
This table isn’t just about specs—it’s a manifesto for two competing visions of progress.
- How Non Payment Of Your Debt Affect Your Integrity
- Strengthening Fight Against Financial Fraud in Nigeria
- 1.3BN Fraud: Police To Arraign Obanikoro's Son On February 27
- An Abuja-Based Bishop Sentenced To 20 Years Imprisonment For Rape of A Minor
The Ripple Effect: What This Means for AI’s Future
Over the next five years, this rivalry could play out in three acts:
Positive Outcomes
-
Democratized AI: Open-source models like DeepSeek R1 could let startups and researchers punch above their weight. Imagine a 20-person team building a ChatGPT rival in Nairobi or Nairobi.
-
Cost Collapse: If training costs keep falling, AI tools could become as cheap and ubiquitous as email.
-
Faster Innovation: Meta’s Yann LeCun argues that open-source ecosystems accelerate progress by letting developers “stand on the shoulders of giants.”
Negative Consequences
-
Security Risks: Decentralized AI could empower bad actors. A Reuters analysis warns of unregulated models being weaponized for disinformation or cyberattacks.
-
Tech Cold War: The U.S. and China might split into competing AI blocs, fragmenting global standards.
-
Job Market Shocks: Cheap, efficient AI could automate roles faster than economies can adapt.
The Global AI Landscape in 2029: Three Possible Scenarios
-
The Open-Source Revolution: DeepSeek’s model spreads globally, making AI a public good. Silicon Valley giants pivot to niche services.
-
The Great Divide: Competing U.S./China ecosystems emerge, each with incompatible tools and regulations.
-
Hybrid Horizons: A blend of open-source foundations and premium add-ons becomes the norm—think Android vs. iPhone, but for AI.
Conclusion: The New Rules of the AI Game
The lesson here isn’t that China is “winning” AI—it’s that the game itself is changing. Money still matters, but efficiency, collaboration, and agility matter more. As Matt Sheehan of Carnegie Endowment notes, U.S. sanctions accidentally gave China a “gift”: the pressure to innovate frugally.
So, will the next decade belong to the spenders or the savers? The answer might be both—but the real winners will be those who master the balance.
What’s your take? Is open-source AI a rising tide that lifts all boats, or a Pandora’s box we can’t control? Let’s debate in the comments.
What's Your Reaction?