The $500 Billion AI Arms Race: How China’s Open-Source Models Like Alibaba Qwen 2.5 Are Redefining the Game
China is rapidly emerging as a dominant force in the $500 billion AI arms race, leveraging open-source AI models like Alibaba Qwen 2.5 to challenge the West’s proprietary AI systems. As companies like OpenAI, Google, and DeepSeek compete for AI supremacy, China’s approach to democratizing AI access could redefine global AI leadership, innovation, and regulation. This article dives into China’s AI strategy, its economic implications, and the evolving power dynamics in the artificial intelligence landscape.

The $500 Billion AI Arms Race: How China’s Open-Source Models Like Alibaba Qwen 2.5 Are Redefining the Game
The U.S. is betting big on artificial intelligence — really big. With a staggering $500 billion poured into AI development over the past decade, America aims to cement itself as the undisputed leader in this transformative technology. But halfway across the world, China is quietly rewriting the rulebook. Companies like Alibaba and DeepSeek are proving that you don’t need a half-trillion-dollar budget to compete. Instead, they’re leveraging open-source innovation, cost-efficiency, and a “work smarter, not harder” ethos to create models like Alibaba Qwen 2.5 and DeepSeek R1—tools that rival even OpenAI’s best, at a fraction of the cost.
What does this mean for the future of AI? Are we headed toward a democratized tech utopia, or a fractured landscape of competing ideologies? Let’s unpack the showdown between these Chinese underdogs and Western giants—and what it means for the next five years.
Alibaba Qwen 2.5: The Heavyweight Contender
How Does Alibaba Qwen 2.5 Work?
At its core, Alibaba’s Qwen 2.5 is a marvel of modern engineering. Built on a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture, it combines 72 billion parameters—think of these as the model’s “brain cells”—to specialize in tasks ranging from language translation to complex problem-solving. Unlike traditional models that activate all neurons for every task, MoE systems like Qwen 2.5 only engage relevant subsets, making them faster and more efficient.
Trained on over 20 trillion tokens (words or word fragments), Qwen 2.5 has devoured a dataset larger than the entire English Wikipedia—50,000 times over. This vast knowledge base lets it outperform rivals like DeepSeek V3 and even some of OpenAI’s models in benchmarks like LiveCodeBench (scoring 38.7) and GPQA-Diamond (60.1). But here’s the kicker: Alibaba achieved this for just $12 million, a laughable sum compared to the $100 million+ budgets of U.S. projects.
Is Qwen 2.5 Open Source?
Alibaba’s approach to openness is… nuanced. While the company has released some open-source components of Qwen 2.5 (like its 1.8B and 7B parameter versions), the full-fledged Qwen 2.5 Max remains a closed-source, paid API. This hybrid strategy lets Alibaba monetize its premium model while still contributing to the open-source community—a balancing act that reflects China’s broader push for both innovation and control.
Compare this to U.S. giants like OpenAI, which keep their flagship models like GPT-5 under lock and key, and you start to see why China’s strategy is turning heads. As [Microsoft’s Brad Smith noted](https://blogs.microsoft.com/on-the-issues/2025/01/03/the-golden-opportunity-for-american-ai/), America’s closed-door approach risks ceding ground to more collaborative global players.
DeepSeek R1: The People’s Champion
If Qwen 2.5 is the polished corporate titan, DeepSeek R1 is the scrappy startup darling. Developed for a mere **$6 million**, this fully open-source model punches far above its weight. With a lean architecture optimized for speed and a pricing model that’s **200x cheaper** than Qwen 2.5 ($0.14 per million input tokens vs. Alibaba’s $10), DeepSeek R1 is built for developers who want powerful AI without the Silicon Valley price tag.
But don’t mistake affordability for weakness. In benchmarks, R1 trails Qwen 2.5 by just 4% in Arena-Hard scores (85.5 vs. 89.4)—a gap small enough to make even the most seasoned AI engineer sweat. Its secret? A relentless focus on efficiency. While Alibaba throws computational brute force at problems, DeepSeek fine-tunes its algorithms to do more with less.
DeepSeek R1 vs Alibaba Qwen 2.5: A Side-by-Side Showdown
Let’s break down how these two models stack up:
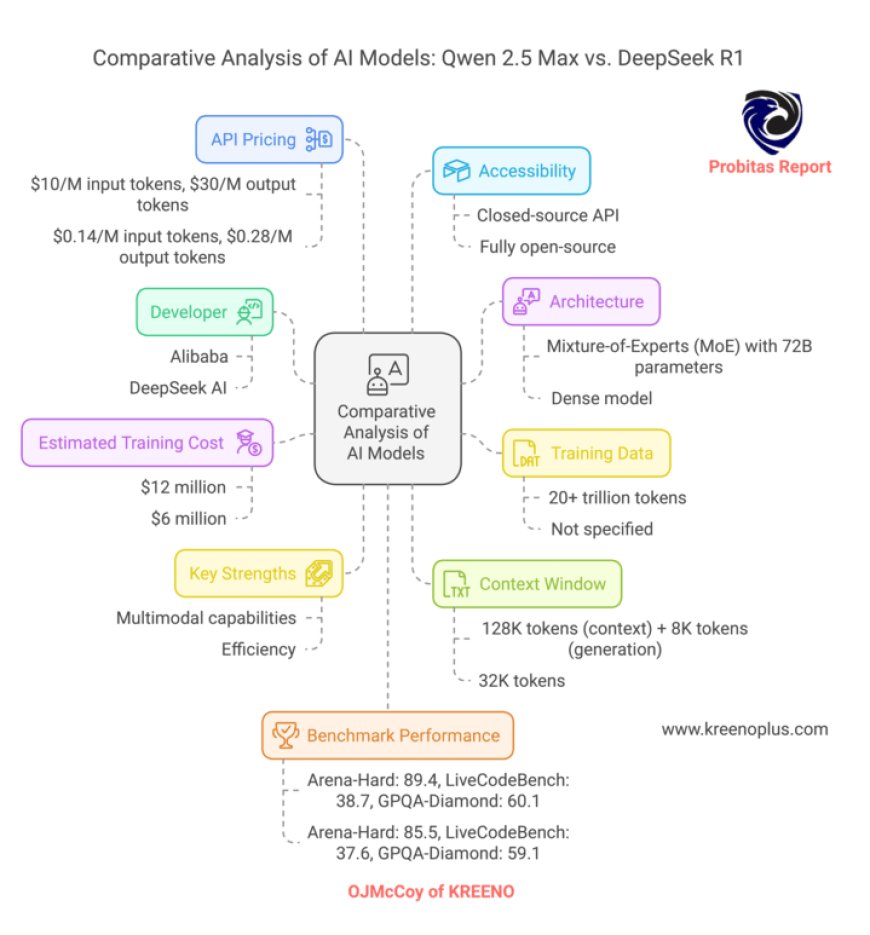
Source: Comparative data synthesized from [Gupta Deepak’s analysis](https://guptadeepak.com/alibabas-qwen-2-5-max-the-ai-marathoner-outpacing-deepseek-and-catching-openais-shadow/) and [The Register](https://www.theregister.com/2025/01/30/alibaba_qwen_ai/).
The takeaway? Qwen 2.5 is the Swiss Army knife—versatile but pricey. DeepSeek R1 is the pocketknife—smaller, sharper, and accessible to all.
The Good, The Bad, and The Geopolitical
Positive Implications
1. Democratization of AI
Open-source models like DeepSeek R1 are tearing down barriers to entry. A startup in Lagos or Lima can now access cutting-edge AI tools without begging venture capitalists for millions. As [Al Jazeera reports](https://www.aljazeera.com/economy/2025/1/28/why-chinas-ai-startup-deepseek-is-sending-shockwaves-through-global-tech), this is already revolutionizing sectors from Nigerian fintech to Indonesian agriculture.
2. Innovation at Warp Speed
Competition breeds creativity. With China forcing efficiency, U.S. labs are rethinking their “burn cash, then burn more” playbook. The result? Breakthroughs like sparse training (teaching AI to learn from less data) are gaining traction.
3. Global Collaboration (Maybe?)
Despite tensions, projects like Qwen’s open-source tiers show that cross-border collaboration isn’t dead. As [Carnegie Endowment notes](https://carnegieendowment.org/research/2025/01/deepseek-and-other-chinese-firms-converge-with-western-companies-on-ai-promises?lang=en), shared challenges like climate change could push rivals toward uneasy partnerships.
Negative Implications
1. The New Cold War
AI isn’t just about chatbots—it’s about power. China’s rise threatens America’s grip on tech standards, from semiconductor design to data governance. The [Washington Post warns](https://www.washingtonpost.com/business/2025/01/28/china-ai-models-usa-technology/c0075a70-dd62-11ef-8889-d5c3924edafd_story.html) this could splinter the internet into “AI blocs” with competing rules.
2. Security Nightmares
Open-source AI is a double-edged sword. While DeepSeek R1 empowers startups, it also lets bad actors build deepfake factories or autonomous hacking tools. China’s [recent AI regulations](https://carnegieendowment.org/research/2025/01/deepseek-and-other-chinese-firms-converge-with-western-companies-on-ai-promises?lang=en) aim to curb misuse, but enforcement remains spotty.
3. Market Mayhem
If Chinese models undercut U.S. prices by 90%, how will Google or Microsoft compete? Layoffs, consolidation, and a “race to the bottom” on pricing could follow—great for consumers, brutal for workers.
READ More News:
- The Acting Group CEO of Access Holdings PLC
- Blackmail And Extortion In Nigeria And Consequences
- Tribute To Mrs Titilayo Osuntoki HCIB
- ABUAD Business School and KREENO Forged Strategic Partnership
The Next Five Years: Collaboration, Conflict, or Both?
By 2029, the AI landscape will look radically different. Here’s what to watch:
- The Open-Source Surge: Expect more hybrid models like Qwen 2.5—partly open, partly proprietary. As [Forbes outlines](https://www.forbes.com/sites/markgreeven/2024/12/23/china-and-ai-in-2025-what-global-executives-must-know-to-stay-ahead/), this lets China shape global standards while retaining control.
- Ethics as a Battleground: Will the U.S. and China agree on AI safety? Unlikely. But watch for grassroots efforts—like the [Open Source AI Alliance](https://www.datacamp.com/blog/qwen-2-5-max) —to bridge the gap.
- The Rise of the “Rest”: Countries like India and Brazil won’t just adopt Chinese or American AI—they’ll remix it. Nigeria’s fintech boom, powered by tools like DeepSeek R1, is just the start.
Final Thoughts: Beyond the Hype
The U.S.-China AI race is often framed as a high-stakes showdown between two tech titans, but the reality is far more nuanced. While Alibaba’s Qwen 2.5 and DeepSeek’s R1 are indeed challenging Western dominance, they’re also democratizing access to tools that were once the exclusive playground of Silicon Valley elites. This isn’t just a story of geopolitical rivalry—it’s a glimpse into a future where AI reshapes economies, empowers marginalized communities, and forces us to confront existential questions about ethics, control, and what it means to be human.
Let’s dig deeper.
The Democratization of AI: A Double-Edged Sword
Open-source models like DeepSeek R1 and partially open frameworks like Alibaba Qwen 2.5 are tearing down barriers to entry. Consider Nigeria’s bustling fintech scene: startups like Flutterwave and Paystack are using R1’s affordable API ($0.14 per million tokens) to build fraud detection systems that rival those of Wall Street banks—at 1/10th the cost. In Indonesia, farmers are experimenting with Qwen 2.5’s multilingual capabilities to optimize crop yields using AI-driven climate models. These aren’t niche experiments; they’re proof that AI is becoming a global toolkit, not a Western monopoly.
But accessibility comes with risks. The same open-source code that powers Nigerian fintech can also be tweaked to create deepfake scams or automate disinformation campaigns. As [The Washington Post reported](https://www.washingtonpost.com/business/2025/01/28/china-ai-models-usa-technology/c0075a70-dd62-11ef-8889-d5c3924edafd_story.html), Chinese models have already been implicated in “AI propaganda factories” targeting Southeast Asian elections. The genie is out of the bottle—and we’re all scrambling to figure out how to live with it.
Job Displacement and the Human Cost
Let’s talk about the elephant in the room: AI is coming for jobs. A [2025 Forbes study](https://www.forbes.com/sites/markgreeven/2024/12/23/china-and-ai-in-2025-what-global-executives-must-know-to-stay-ahead/) estimates that 20% of global customer service roles could vanish by 2030, replaced by chatbots built on models like Qwen 2.5. In manufacturing, Chinese firms are already using R1-powered robots to automate factories at a pace that’s left Western competitors reeling.
But this isn’t just a story of loss. The same models displacing workers are also creating opportunities. In Kenya, developers are fine-tuning R1 to diagnose crop diseases from smartphone photos, creating new roles for “AI agriculture consultants.” In healthcare, Qwen 2.5’s advanced reasoning helps Indian doctors interpret MRIs faster, freeing them to treat more patients. The challenge isn’t stopping AI—it’s ensuring the benefits are shared equitably. As Microsoft’s Brad Smith [argued](https://blogs.microsoft.com/on-the-issues/2025/01/03/the-golden-opportunity-for-american-ai/), “The nations that invest in retraining—not just R&D—will dominate the next economy.”

Algorithmic Bias: Who’s Responsible?
Here’s an uncomfortable truth: AI models mirror the biases of their creators. When Alibaba Qwen 2.5 was tested for hiring recommendations, researchers found it disproportionately favored candidates from elite Chinese universities. Similarly, early versions of DeepSeek R1 struggled with gender bias in languages like Arabic, where pronouns are more complex.
But open-source models offer a unique advantage: transparency. Unlike closed systems like GPT-5, R1’s code can be audited and adjusted by anyone. A collective of Tunisian developers recently patched R1’s Arabic bias issues and shared their fix on GitHub—a grassroots solution that would’ve been impossible with proprietary software. As [Carnegie Endowment notes](https://carnegieendowment.org/research/2025/01/deepseek-and-other-chinese-firms-converge-with-western-companies-on-ai-promises?lang=en), this “crowdsourced ethics”approach could become AI’s best defense against bias... if we embrace it.
Security in the Age of Open-Source AI
Security experts are losing sleep over models like R1. In 2023, hackers used a modified version of the algorithm to generate phishing emails that bypassed Google’s spam filters, stealing $2 million from small businesses. Meanwhile, state actors are weaponizing Qwen 2.5’s multimodal capabilities to create hyper-realistic propaganda videos.
But closed-source AI isn’t inherently safer. When OpenAI’s GPT-4 was hacked in 2024, the company took weeks to patch the漏洞—a delay that wouldn’t have happened with open-source models where fixes can be deployed in real-time by the community. The lesson? Security isn’t about locking down AI; it’s about building resilient, adaptable systems. China’s [new AI regulations](https://carnegieendowment.org/research/2025/01/deepseek-and-other-chinese-firms-converge-with-western-companies-on-ai-promises?lang=en), which mandate “ethical training data” and real-time monitoring, offer a blueprint—but enforcement remains spotty.
Governance: The Global Power Struggle
The U.S. and China aren’t just competing for AI supremacy—they’re fighting to write the rulebook. China’s 2025 AI Governance Act imposes strict rules on data privacy and algorithmic transparency, while the U.S. remains stuck in regulatory gridlock. The EU’s AI Act, with its focus on human rights, adds a third voice to the chorus. This patchwork of policies creates chaos for global companies. A medical AI trained on Qwen 2.5 might comply with Chinese laws but violate EU patient privacy standards. DeepSeek R1’s open-source nature lets developers skirt restrictions entirely, raising thorny questions: *Can you regulate code that’s freely available everywhere?*
The Road Ahead: Collaboration or Collision?
Over the next five years, two scenarios could unfold:
1. The Balkanization of AI: The U.S. and China decouple their tech ecosystems, creating incompatible AI “spheres.” Qwen 2.5 dominates Asia and Africa, while Western models rule elsewhere. Startups are forced to pick sides, stifling innovation.
2. The Open-Source Renaissance: Rival models like R1 and Qwen 2.5 converge into a global “AI commons,” similar to how Linux united the open-source software movement. International bodies like the UN set baseline ethics standards, while companies compete on implementation. The likely outcome? A messy middle ground. We’ll see pockets of collaboration—like the [Open Source AI Alliance](https://www.datacamp.com/blog/qwen-2-5-max), which includes players from both China and Silicon Valley—amid fierce competition for market share.
- How Non Payment Of Your Debt Affect Your Integrity
- Strengthening Fight Against Financial Fraud in Nigeria
- 1.3BN Fraud: Police To Arraign Obanikoro's Son On February 27
- An Abuja-Based Bishop Sentenced To 20 Years Imprisonment For Rape of A Minor

Conclusion: Steering the Ship
As we stand at this crossroads, one thing is clear: AI’s future isn’t predetermined. Models like Alibaba Qwen 2.5 and DeepSeek R1 have given us the tools to build a more equitable world—or deepen existing divides. The choice comes down to three priorities:
1. Invest in People, Not Just Technology: Instead of allocating the entire $500 billion AI budget solely to technological advancements, a portion should be redirected toward global education, workforce retraining, and skill development programs. Likewise, every country should commit a dedicated percentage of their annual budget to retooling, relearning, and reskilling their workforce. This investment should extend beyond traditional education by revamping secondary and tertiary institution curricula to align with the evolving demands of the digital and AI-driven economy. Without this shift, the gap between technological progress and human adaptability will continue to widen, leaving many behind in the future workforce.
2. As artificial intelligence becomes increasingly integrated into our society, the need for ethical guardrails and inclusive governance has never been more critical. Let's explore two key strategies to ensure AI benefits humanity as a whole:
Building Ethical Guardrails through Transparent Auditing Frameworks
To combat bias, misuse, and ethical violations in AI systems, we need to establish open-source auditing frameworks that enable real-time detection of potential risks. These frameworks should be transparent and publicly accessible, allowing independent researchers, policymakers, and civil rights organizations to monitor AI systems for fairness and accountability[1].
One approach is to utilize AI ethics scorecards and bias detection algorithms to assess whether models disproportionately impact certain demographics. For instance, researchers have developed tools that can automatically identify and mitigate biases in datasets, such as Microsoft's efforts to reduce recognition errors in their Face API[8].
These frameworks should be universally applicable across industries, from financial services to healthcare, ensuring AI remains a tool for equity rather than discrimination. The Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA) has developed a comprehensive AI Auditing Framework that covers various aspects, including cyber resilience, AI competencies, and ethical AI considerations[3].
Importantly, these frameworks should allow for real-time intervention mechanisms, where problematic AI behavior can be flagged and corrected before causing harm. By embedding ethical oversight into AI from the start, we can prevent unintended consequences and ensure that technology serves humanity's best interests rather than exacerbating inequalities[2].
3. Democratizing AI Decision-Making
AI governance cannot be dictated solely by a handful of technologically dominant nations. For AI to truly benefit the world, developing nations must be active participants in shaping its policies, not passive bystanders.
This requires equal representation in AI policy forums, such as the United Nations AI Advisory Body, OECD AI Policy Observatory, and AI safety summits. It's crucial to invest in AI research and education in the Global South, ensuring that developing nations own and control their technological futures rather than relying on external AI solutions[7].
One proposal is to establish a global AI fund where wealthier nations contribute resources to help lower-income countries develop homegrown AI expertise and infrastructure. This approach could help bridge the technological divide and ensure more diverse perspectives in AI development[6].
Additionally, mandating corporate AI accountability is essential – forcing tech companies to adhere to ethical AI standards globally, not just in select jurisdictions. Companies like Microsoft and Google have already taken steps in this direction by forming AI ethics committees and introducing transparency measures like Google's Model Card function[8].
Without an inclusive approach, AI risks further widening the economic and technological divide. True democratization means ensuring every nation – not just the AI superpowers – has a voice in shaping the future of artificial intelligence[5].
By implementing these strategies, we can work towards an AI future that is both ethical and inclusive, benefiting all of humanity rather than exacerbating existing inequalities.
Citations:
[1] https://www.centraleyes.com/ai-auditing/
[2] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8830968/
[3] https://www.auditboard.com/blog/ai-auditing-frameworks/
[4] https://www.acrolinx.com/blog/inclusivity-and-algorithmic-bias/
[5] https://codewave.com/insights/ai-auditing-framework-understanding/
[6] https://insight7.io/ai-tools-for-research-bias-detection/
[7] https://www.fairly.ai/blog/policies-platform-and-choosing-a-framework
[8] https://www.nature.com/articles/s41599-023-02079-x
The next five years will test whether humanity can wield AI’s power wisely. But if history is any guide, it’s not the technology we should fear—it’s our inability to imagine a better way forward. Buckle up, stay curious, and keep your moral compass close. The ride’s just beginning.
For further reading on China’s AI strategy, explore [Carnegie’s analysis](https://carnegieendowment.org/research/2025/01/deepseek-and-other-chinese-firms-converge-with-western-companies-on-ai-promises?lang=en) or dive into Qwen 2.5’s technical specs via [DataCamp](https://www.datacamp.com/blog/qwen-2-5-max).
Author:
Dr. Ohio O. Ojeagbase, FICA, FIDR (a.k.a Dr Kreeno)
Chief Private Investigator/CEO
Kreeno Debt Recovery and Private Investigation Agency
A Subsidiary of KREENO Holdings LLC, USA

Kindly share this story:
Contact: report@probitasreport.com
Stay informed and ahead of the curve! Follow The ProbitasReport Online News Report on WhatsApp for real-time updates, breaking news, and exclusive content especially when it comes to integrity in business and financial fraud reporting. Don't miss any headline – and follow ProbitasReport on social media platforms @probitasreport
[©2025 ProbitasReport - All Rights Reserved. Reproduction or redistribution requires explicit permission.]
What's Your Reaction?